Introduction
Aluminum (Al), as AAHS (amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate), aluminum hydroxide, or aluminum phosphate, is used as an adjuvant in a number of inactivated and subunit vaccines in order to provoke an immune response. While aluminum has no purpose in the human body and is a known toxin, there have been no studies to determine a safe level of aluminum, or of most other ingredients, in vaccines. Instead, the allowable amounts of aluminum that are sometimes used as a guideline for safety reviews, refer to allowable amounts of dietary aluminum. An infant (even one who is premature) is injected on day 1 with the Hepatitis B vaccine; a newborn of average birth weight will receive a 17-fold greater amount of aluminum than it would have had the amount been adjusted for body weight. Far from being a harmless adjuvant, aluminum poses serious health consequences for many vaccinees.
Key Points
- Aluminum adjuvants are promoted as safe and effective, yet:
- Scientists have been aware of aluminum toxicity as early as 1921
- The World Health Agency lists aluminum as a cause of neurodevelopmental disorders
- Aluminum is particularly dangerous for infants, the elderly, and those with impaired renal function
- Individuals involved in vaccine science, including vaccine manufacturers, do not fully understand metals or have knowledge of toxicological research
- Aluminum’s mechanism of action is not well understood.
- Up to .85 mg of aluminum are allowed in each vaccine dose, per the FDA. Scientists do not know how this figure was arrived at.
- There have been no studies to determine a safe limit of injected aluminum
- Weak studies are used to justify the use of aluminum in vaccines and the vaccine schedule
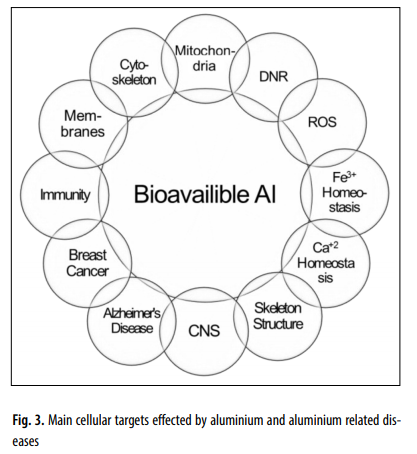
- Aluminum deranges body chemistry.
- Aluminum:
- Inhibits over 200 important biologically important functions
- Interferes with the body’s use of calcium, magnesium, Vitamin K, and hydrogen
- Induces DNA damage
- Interrupts bone formation resulting in spontaneous fractures
- Can accumulate in the body when bypassing the gastrointestinal barrier (as with vaccines), resulting in aluminum overload
- Negatively impacts the male reproductive system
- Aluminum has been found to cause severe and chronic illness including:
- Encephalopathy (brain disease), dementia and impaired neurological development, osteopenia (low bone density), and osteomalacia (softening of bones to do impaired bone metabolism)
- Macrophagic myofasciitis (MMF)
- Allergy to aluminum
- Aluminum induced bone disease
- Many autoimmune/inflammatory diseases
- Autism; aluminum is found in excessive amounts in the brains of autistic individuals
- Epilepsy
- Concurrent exposure to both aluminum and mercury may have added dangers
